Monosaccharides are considered the exceptional styles of carbohydrates that may be termed as “easy sugars.” These are constructing blocks to shape greater complicated structures of carbohydrates that need to exist in all residing organisms. So what happens even as monosaccharides meet? What is the macromolecule for monosaccharide, and the way does this take place? We describe the biochemical pathway through which monosaccharides combine to shape huge macromolecules. Apart from this, we similarly define unique varieties of macromolecules, the structures of monosaccharides, and the manner those macromolecules feature in the body.
Structure of Monosaccharides
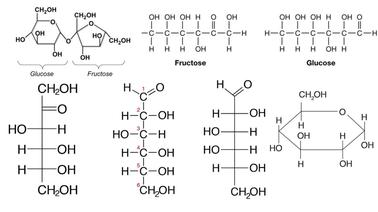
Before we describe the macromolecule made from monosaccharides, allow’s outline what a monosaccharide is. A monosaccharide is one molecule composed of carbon atoms (C), hydrogen atoms (H), and oxygen atoms (O). Three of the common monosaccharides are glucose, fructose, and galactose. While all fit the general method C₆H₁₂O₆, there can be a distinction in how the atoms are arranged:.
Monosaccharides, which might be usually ring-fashioned whilst in solution in water, are the handiest carbohydrates. Because monosaccharides are so easy, they effects can be cleaved to supply or combined with exclusive molecules to yield large and more complicated structures. Two monosaccharides joined collectively yield disaccharides, even as many monosaccharides yield polysaccharides,macromolecules collectively with sugars.
Types of Macromolecules in Biology
Macromolecules are huge, complex molecules crucial to life, which are composed of smaller gadgets known as monomers. Four training of natural macromolecules exist primarily based on the shape of monomers and their popular structures.
- Proteins: Made of amino acids.
- Nucleic Acids: Made of nucleotides (DNA and RNA).
- Lipids: Made of fatty acids and glycerol.
- Carbohydrates: Made of monosaccharides, along with glucose and fructose.
Here we will cover carbohydrates and the way monosaccharides increase into the massive carbohydrate macromolecules called polysaccharides.
Macromolecule of Monosaccharide
The macromolecule crafted from monosaccharides is a polysaccharide. Polysaccharides are big chains of monosaccharides joined through glycosidic bonds. Such big macromolecules may be very long, and often can have several functions in residing organisms.
There are some examples on this list; among them are starch, cellulose, and glycogen. The former is used for starches, and the latter is used for glycogens thru animals. Cellulose systems help inner plant cellular walls.
How Are Monosaccharides Converted to Polysaccharides?
What is the macromolecule for monosaccharide?, This biochemical system of becoming a member of many monosaccharide molecules together to make a polysaccharide is called dehydration synthesis, or condensation. During this technique, water is misplaced whenever monosaccharide molecules integrate. The combining of these molecules then creates a glycosidic bond that holds the monosaccharide molecules collectively.
For example, even as glucose molecules combine, they produce the disaccharide maltose. When many glucose molecules connect to every other they form starch (in flora) or glycogen (in animals), which each act as storage molecules for energy.
Structure of Carbohydrate Macromolecule
The shape of carbohydrate macromolecules differs significantly depending upon the form of polysaccharide. For instance:
Starch is a plant garage polysaccharide and paperwork prolonged chains of glucose molecules branching out in areas.
- Glycogen: Similar to starch, is the garage form of glucose in animals. Though made out of glucose devices, it has many more branches than starch.
- Cellulose: Is the structural polysaccharide of plant cell partitions. It is, geometrically, a
protracted immediately molecule composed of chains of glucose molecules related with the aid of the use of hydrogen bonds. This affords strain and strength to a plant.
In a majority of these instances, the monosaccharides, like glucose, are joined collectively to create extra complicated systems having special roles in living organisms.
Role of Carbohydrates in Cells
Carbohydrates play several key capabilities in cells and living organisms:
Source of Energy:
Monosaccharides such as glucose are one of the most critical resources of strength in cells. They wreck inner particular strategies including glycolysis and cell respiration, which damage unfastened the power stored inside the chemical bonds of these monosaccharides.
Energy Storage:
Polysaccharides, which includes starch and glycogen, have strength saved in them for later use. Whenever the frame desires electricity, the polysaccharides break down into monosaccharides that strengthen metabolic techniques.
Structural Support:
Polysaccharides like cellulose give structural aid in vegetation with the useful resource of forming hard cellular partitions. Another carbohydrate, chitin, offers structures to exoskeletons of arthropods and insects.
Cell Signaling:
Carbohydrates also are a part of cell signaling or communique. Glycoproteins are proteins which include carbohydrate chains bonded to them. They play a function in immune reactions and cellular recognition.
Examples of Macromolecules with Monosaccharides
The following are some illustrative examples of macromolecules containing monosaccharides:
- Starch: Containing glucose, starch is the predominant storage polysaccharide in plant life.
- Glycogen: Much more rather branched than starch, glycogen is the garage shape of glucose in animals.
- Cellulose: A structural polysaccharide in flowers, which offers cells energy and anxiety.
- Chitin: A polysaccharide that forms an awful lot of the structural component of exoskeletons in arthropods and mobile partitions in fungi.
- Peptidoglycan: A carbohydrate-protein complicated composing bacterial cell walls.
Monosaccharides vs. Polysaccharides
The important difference among the 2 kinds of carbohydrates is complexity. Monosaccharides are single molecules which can be absorbed extraordinarily rapid by way of the use of the frame so you can supply power. They encompass glucose, fructose, and galactose. Polysaccharides, alternatively, encompass many devices of monosaccharides. Such big molecules take plenty greater time to digest and supply slower energy supply. Some polysaccharides moreover provide structural features: cellulose in plant life and chitin in animals.
How does jelly react with monosaccharides?
How dose jelly react with monosaccharides?The most commonplace carbohydrate polymer applied in making geared up jelly is referred to as pectin. The glucose and fructose in fruit juices react with pectin while the juices are cooked. Heat kills the cellular walls of fruit, breaking them aside and freeing pectin, which could gel if sure to sugars and water. This gel gives jelly its thickness and is the combined sugar and pectin that the very last product is nice and has its shape.
Conclusion
Polysaccharides, put sincerely, are the fabricated from polymerization of monosaccharides.What is the macromolecules for monosaccharide?, Complex carbohydrates-the ones are large molecules that perform numerous roles in the organism.Also including garage of power, structural guide, signaling amongst cells, and many others. Monosaccharides function by constructing blocks of polysaccharides. The biochemical pathway from easy sugars to complicated carbohydrate structure explains why carbohydrates are critical in existence.
0 Comments